Relative Mass
What are the exact relative masses of protons, neutrons and electrons?
Protons and neutrons have nearly the same mass while electrons are much less massive. If we assume that a neutron has a mass of 1, then the relative masses are:
Neutron = 1
Proton = 0.99862349
Electron = 0.00054386734
Said another way, protons are only about 99.86% as massive as neutrons while electrons are only about 0.054% as massive as neutrons. While relative masses are nice if you want to compare protons, neutrons and electrons to one another, it doesn't tell you what the actual masses of these particles are. In kilograms, the masses are:
- The relative mass of anchor is 3, meaning that it is three times greater than one of the other objects. Since the objects are listed in descending order, the value for anchor has to be not greater than 7.64. The only way you get this is by multiplying 3 times the mass of the washer, which would equal 5.22.
- The relative mass of a Proton = 1. The relative mass of a Neutron= 1. The relative mass of Electron = 1/1840 = 0.0005. Characteristics of Electron. The antiparticle of Electron is; The spin of the electron – ½; Electric charge = -1; Hope that you have known the important information about the mass of the electron.
Neutron = 1.6749286*10-27 kg
Proton = 1.6726231*10-27 kg
Electron = 9.1093897*10-31 kg
There is another unit, called an electron volt (eV), that scientists use when talking about small things like protons, neutrons and electrons. An electron volt is actually a measurement of energy, but scientists can get away with using it to measure mass since mass and energy are related by Einstein's famous equation, E = mc2. So, in terms of MeV (Megaelectron volts, 1 MeV = 1,000,000 eV), the masses are:
Relative isotopic mass is known to be the relationship between the mass of an isotope of an element relative to the mass of an isotope of the atom.
Neutron = 939.56563 MeV
Proton = 938.27231 MeV
Electron = 0.51099906 MeV
Author:
Steve Gagnon, Science Education Specialist (Other answers by Steve Gagnon)
Related Pages:
For questions about this page, please contact Steve Gagnon.
Also found in: Thesaurus, Medical, Financial, Acronyms, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
relative atomic mass
n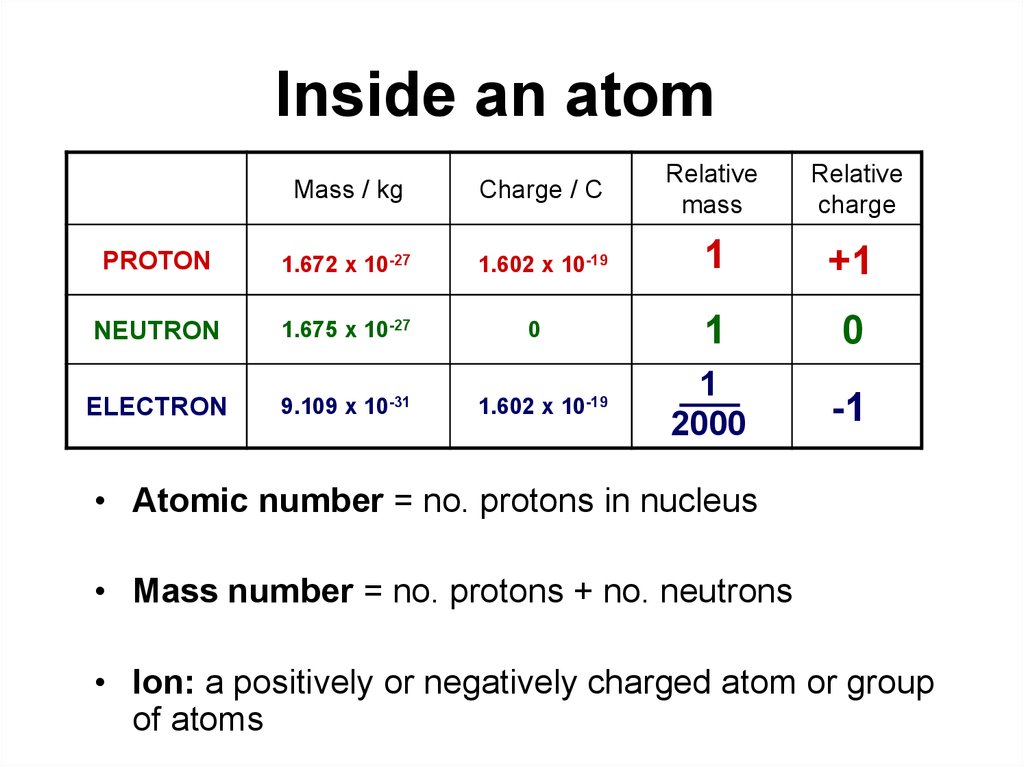
relative atomic mass
| Noun | 1. | relative atomic mass - (chemistry) the mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units atomic mass, atomic weight mass - the property of a body that causes it to have weight in a gravitational field combining weight, eq, equivalent weight, equivalent - the atomic weight of an element that has the same combining capacity as a given weight of another element; the standard is 8 for oxygen meq, milliequivalent - one-thousandth of an equivalent chemical science, chemistry - the science of matter; the branch of the natural sciences dealing with the composition of substances and their properties and reactions |
How To Calculate Relative Formula Mass

 Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content.
Want to thank TFD for its existence? Tell a friend about us, add a link to this page, or visit the webmaster's page for free fun content. Link to this page:

Relative Mass Calculator

Relative Mass
